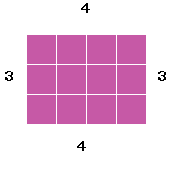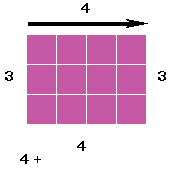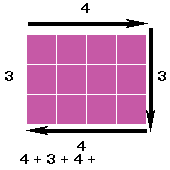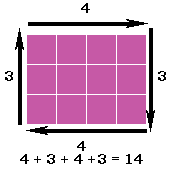Area
المقررات الدراسية موسومة بـ "Area"
Internet of Things
In this course , learn about the internet of things and its purpose.
Introduction
These definitions will help during this course:· RFID – Radio Frequency Identification
· IP – Internet Protocol, a set of rules defining the format of data transferred over the internet or network
· Broadband Internet – an internet connection with a high data transfer rate
· Cellular Network – a radio network distributed over cells each served by a base station
· Wireless Network – a network that uses wireless data connections between nodes
The Internet of Things (IoT) is the term applied to everything connected to the internet. It is increasingly being used to define objects that talk to each other. These devices range from sensors to smartphones and wearable technology (e.g. FitBit or Apple Watch).
The IoT enables devices on private networks to communicate with others. This in turn, creates a more connected world across multiple different network types.
You will learn
- Look at the fundamentals of the Internet of Things
- Investigate how the Internet of Things can be enabled for all users
Units of Measurement
Introduction
To be able to measure something, you need to know what unit to use. A unit is a general term that means a type of measurement.A unit is any measurement that there is 1 of, such as:
· 1 metre
· 1 second
· 1 metre per second (1 m/s)
· 1 gram
· 1 square centimetre (1 cm2)
Units of measurement are standardised, meaning that there is a well-defined way to measure them.
We can use both metric and imperial units of measurement to measure things such as length, weight and capacity. Below are examples of units used in the metric and imperial systems:
Metric
· Length – units include millimetres, centimetres, metres and kilometres.
· Weight – units include grams and kilograms.
· Capacity – units include millilitres and litres.
Imperial
· Length – units include inches, feet, yards and miles.
· Weight – units include ounces, pounds and stone.
You will learn
- Be able to identify imperial and metric measures commonly used in the UK
- Understand when different units of measurement are used in everyday contexts
- Know the abbreviations for commonly used imperial and metric units of measurement
- Be able to convert between imperial units
- Be able to convert between metric units
Temperature
Learn about temperature, how to identify, read and compare thermometers used for different purposes and with different scales. This course is ideal for intermediate learners.
Introduction
Temperature refers to how hot or cold something is.Temperature is measured in degrees. The symbol for degrees is a small circle that sits slightly above the number in temperature.
The two most common scales are Celsius (°C) and Fahrenheit (°F). In the UK, we usually measure temperature in Celsius (°C).
On a standard thermometer, the left hand side measures temperature in Celsius, ranging from 0 (freezing point) to 100 (boiling point). The right hand side measures temperature in Fahrenheit, ranging from 32 (freezing point) to 112 (boiling point).
We measure temperature using a mechanical or electrical device called a thermometer. There are lots of different types of thermometer.
Thermometers may be digital or analogue.
A digital thermometer gives a reading in figures and an analogue thermometer uses a scale.
You will learn
- Identify, read and compare thermometers used for different purposes and with different scales
- Read scales to the nearest labelled and unlabelled division
- Read positive and negative temperatures
- Solve simple problems relating to temperature
Subtraction
Learn about subtraction, subracting three digit numbers and subtracting using a range of methods. This course is ideal for intermediate learners.
Introduction
When you subtract numbers you use the subtraction sign. It is a small horizontal line.We use different words to describe subtraction.
For example, can be described as:
· 25 subtract 6 equals 19
· The difference between 35 and 6 is 29
· 30 take away 10 is 20
· 30 minus 10 is 20
· 19 is 6 less than 25
· If you decrease 25 by 6 you get 19
Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. Subtraction is signified by the minus sign.Subtraction follows several important patterns. It is anticommutative, meaning that changing the order changes the sign of the answer. It is also not associative, meaning that when one subtracts more than two numbers, the order in which subtraction is performed matters.
You will learn
- Subtract three-digit numbers
- Subtract using a range of methods
Perimeter
Learn about perimeter, what it is, understand units of length used to measure preimeter and how to use different methods to find the perimeter of a range of shapes. This course is ideal for intermediate learners.
Introduction
The perimeter is the distance around the edge of a shape.Here are some examples of when we may need to find the perimeter of a shape in everyday life:
· Making a picture frame
· Putting a border around a cushion
· Fitting a rail around a room
You will learn
- Know what perimeter is
- Understand units of length used to measure perimeter
- Be able to use different methods to find the perimeter of a range of shapes
Decimals
Learn about decimals and understanding the use of decimal place values and digits. This course is ideal for intermediate learners.
Introduction
Decimal numbers break down whole numbers into smaller parts. They always have a decimal point.The decimal point separates the whole numbers from parts of whole numbers.
The two digits after the decimal point are tenths and hundredths.
The breakdown of a decimal is as follows:
Tens, Units (ones), Decimal Point, Tenths, Hundredths
You will learn
- Understand the use of decimal place values and digits
- Understand how zero is used as a placeholder for decimal numbers
- Be able to use decimals in different contexts
- Be able to write decimals in word and digit form
- Be able to compare the size of decimals
Averages and Range
Learn about averages and range, understanding the difference between the mean, median and mode and how to find the mean value and the range. This course is ideal for intermediate learners.
Introduction
Average is a value that is typical of a set of numbers.You can compare two sets of numbers by comparing the averages of the sets. For example, you could compare the performance of two hockey teams by looking at the average number of goals scored by each team.
There are three main ways to measure the average:
· Mean
· Median
· Mode
In this course we will look at each type of average. It is important to understand all three averages, although at the moment you only need to be able to calculate the mean.
However, Range is the difference between the highest and lowest values in a set of data. The difference between the highest and the lowest values in the given set of data is called the 'range' of the data.
You will learn
- Understand the difference between the mean, median and mode
- Find the mean value
- Find the range
Area
Learn about area, the meaning, how to work out areas by counting and calculating and solve simple problems involving area. This course is ideal for intermediate learners.
Introduction
Area is the space on a flat surface. It is measured in square units.
A square measures 1 cm high and 1 cm wide. It is 1 square centimetre (the shortened version are the letters c and m with a small number two placed just above the m, which represents squared).
There are many different units of measurement that can be used to measure area.Square millimetres
There are 10 millimetres in a centimetre. A square millimetre is millimetres times by millimetres, which is written mm² (the letters m and m, with the squared symbol).
Square centimetres
There are 100 centimetres in a metre. A square centimetre is centimetre times by centimetre, which is written cm² (the letters c and m, with the squared symbol).
Square metres
There are 1,000 metres in a kilometre. A square metre is metres times by metres, which is written m² (the letter m, with the squared symbol).
Square kilometres
A kilometre is equal to 1,000 metres. A square kilometre is kilometre times by kilometre, which is written km² (the letters k and m, with the squared symbol).
You will learn
- Understand the meaning of area
- Be able to work out areas by counting and calculating
- Be able to solve simple problems involving area
Areas
Learn about areas, specifically calculating the area of a rectangle and triangle and working out areas in practical situations. This course is ideal for beginners.
Intorduction
Area is the space on a flat surface.It is measured in square units.
For example, a square that measures 1 cm long and 1 cm wide is 1 square centimetre (the shortened version are the letters c and m with a small number two placed just above the m, which represents squared).
There are many different units of measurement that can be used to measure area.
For example, you can measure area in:
Square millimetres
There are 10 millimetres in a centimetre. A square millimetre is millimetres times by millimetres, which is written mm² (the letters m and m, with the squared symbol).
You will learn
- Calculate the area of a rectangle
- Calculate the area of a triangle
- Work out areas in practical situations
Perimeter and Area
In this course, learn the skills that are needed to understand the space around us.
Introduction
This badge focussed on two of those space-related skills – Perimeter and Area.The perimeter of any shape is the distance around the outside. That distance is useful in many contexts.
You will learn
How to calculate the perimeter of a shape
How to calculate the area of a rectangular shape
How perimeters and areas can be used in real-life situations