Maths
Courses tagged with "Maths"
Units of Measurement
Introduction
To be able to measure something, you need to know what unit to use. A unit is a general term that means a type of measurement.A unit is any measurement that there is 1 of, such as:
· 1 metre
· 1 second
· 1 metre per second (1 m/s)
· 1 gram
· 1 square centimetre (1 cm2)
Units of measurement are standardised, meaning that there is a well-defined way to measure them.
We can use both metric and imperial units of measurement to measure things such as length, weight and capacity. Below are examples of units used in the metric and imperial systems:
Metric
· Length – units include millimetres, centimetres, metres and kilometres.
· Weight – units include grams and kilograms.
· Capacity – units include millilitres and litres.
Imperial
· Length – units include inches, feet, yards and miles.
· Weight – units include ounces, pounds and stone.
You will learn
- Be able to identify imperial and metric measures commonly used in the UK
- Understand when different units of measurement are used in everyday contexts
- Know the abbreviations for commonly used imperial and metric units of measurement
- Be able to convert between imperial units
- Be able to convert between metric units
Rounding and Estimating
Learn about rounding and estimating and unerstanding when it is appropriate to use rounding and estimating and when an exact answer is needed. This course is ideal for intermediate learners.
Introduction
Rounding numbers is a way to get a rough idea or an estimate. An estimate might be a little more or a little less than the exact figure. Rounding means making a number simpler but keeping its value close to what it was.Although rounding won’t give you an exact figure, by carrying out an estimate you can check that the answer to a problem is sensible. For example, it’s a good idea to estimate the answer first when using a calculator in case you make keying errors.
Estimation is also really useful with multiple choice test questions. It helps you decide which option is the correct answer before checking by carrying out calculations.
3 of 20 – Benefits of rounding
Rounding is a really important tool with a number of benefits, including:
· Making it easier to describe and understand numbers
· Making calculations easier
· Making it easier to estimate answers
· Helping you to identify mistakes in maths work
· Being useful when you don’t need an exact answer
You will learn
- Understand when it is appropriate to use rounding and estimating and when an exact answer is needed
- Be able to round to the nearest 10 or 100
- Be able to round and estimate in everyday contexts
Ratios and Proportion
Learn about ratios and proportion, the meaning of ratio and proportion and how to solve simple proportion problems. This course is ideal for intermediate learners.
Introduction
Ratio tells us the size of two amounts compared to each other.Consider four squares – three of them are purple and one of them is green. Here are three ways that we can express this as a ratio:
· We can write it as a fraction. For example, \( \frac{1}{3} \).
· We can separate the values with the word ‘to’. For example, 3 to 1.
· We can use a colon to separate the values. For example, 3:1 (the colon is between the 3 and the 1).
The order of the numbers in a ratio must match the order of the words.
Again, consider the three purple squares and one green square. The ratio of purple squares to green squares is 3 to 1. This means there are three times as many purple squares as green.
However, if we change the order of the words we must also change the order of the numbers in the ratio. For example, the ratio of green squares to purple squares is 1 to 3.
You will learn
- Understand the meaning of ratio and proportion
- Be able to solve simple proportion problems
Place Values and Number Symbols
Learn about place values and number symbols and understanding the meaning of place values. This course is ideal for intermediate learners.
Introduction
Did you know that all numbers are written using only ten digits? Every number that you can think of uses one or more of these digits:0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
For example, 257 is a three-digit number because it has three digits. It can also be called a three-figure number.
Place value
Consider the digit 5 in these numbers:
5, 50, 500, 5000
Whether the 5 stands for five, fifty, five hundred, or five thousand depends on the position of the digit in the number. This is called its place value.
Understanding place value means that we can read any number, however small or big.
To understand place values we can put digits into columns in a place value table, like the one below. These columns are always in the same order.
You will learn
- Understand the meaning of place values
- Know how zero is used as a placeholder
- Be able to write numbers in words and figures
- Be able to use place value to read numbers written in figures
- Be able to use place value to place numbers in order
Multiplication
Learn about multiplication and understand that multiplication is a method of repeated addition. This course is ideal for intermediate learners.
Introduction
Multiplication is a method for adding a number to itself a number of times.This is also called repeated addition.
For example 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 = 12 is the same as 3 multiplied by 4 = 12.
Multiplication is a quicker method of repeated addition, especially when you are multiplying large numbers.
For example 50 + 50 + 50 + 50 + 50 + 50 + 50 + 50 + 50 = 450 is the same as 50 multiplied by 9 = 450.
You will learn
- Understand that mulitplication is a method of repeated addition
- Be able to use a range of mulitplication methods
- Understand how to use place value shortcuts to muplitply by 10, 100 and 1,000
- Be able to solve multiplication problems in everyday settings
Money
Learn about money, how to read, write and express money amounts, write money using word and decimal notation and complete simple calculations involving money. This course is ideal for intermediate learners.
Introduction
Money is one of the most common measurements that we use. Being confident at using money can help in many everyday situations. For example:· Understanding your payslip
· Budgeting for your personal finances
· Paying for things
· Giving people the correct change
· Calculating costs
· Handling money in your job.
You will learn
- Read, write and express money amounts
- Write money using word and decimal notation
- Complete simple calculations involving money
Length and Distance
Learn about length and distance and understanding the difference between standard and non-standard units of measurement for length and distance. This course is ideal for intermediate learners.
Introduction
We can measure length or distance using either standard or non-standard units of measurement.A unit is a general term that means a type of measurement. A unit is any measurement that there is 1 of, such as:
· 1 metre
· 1 yard
· 1 kilometre
Standard units of measurement are standardised, meaning that there is a well-defined standard way to measure 1 of them. We use them when we need exact measurements.
There are two main systems of measurement for length and distance:
· Metric units of length include millimetres, centimetres, metres and kilometres
· Imperial units of length include inches, feet, yards and miles
You will learn
- Understand the difference between standard and non-standard units of measurement for length and distance
- Understand standard units of measurement for length and distance, including metric and imperial units
- Be able to choose appropriate units of measurement and measuring equipment
- Be able to measure the lengths of objects accurately
Fractions
Learn about fractions, understanding that fractions are part of a whole, how to recognise fractions from shapes, express fractions in words and numbers and work out simple fraction problems. This course is ideal for intermediate learners.
Introduction
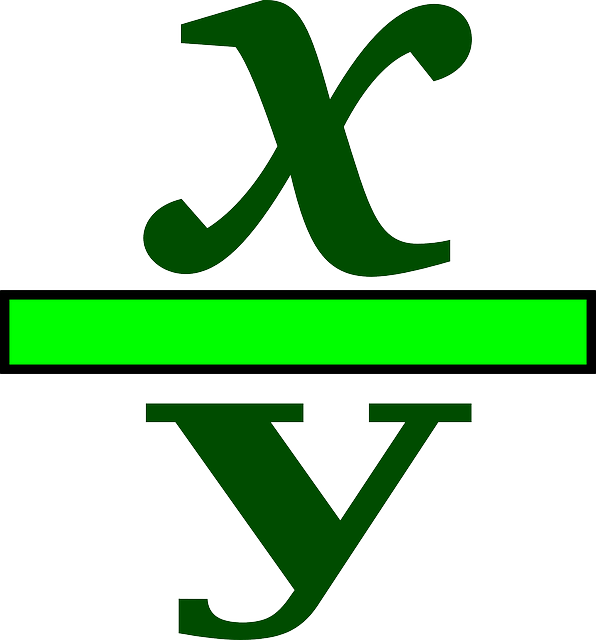
A fraction is a part of something. Fractions are always written as follows:Numerator over denominator. The numerator sits above the horizontal line and the denominator sits below the line. The numerator shows how many parts of the whole are being represented. The denominator shows how many parts make the whole.
Let’s look at an example.We write an eighth as follows: \( \frac{1}{8}\)
The 1 sits above the fraction line and the 8 sits below. Here the numerator is showing that this fraction represents 1 part of the whole. Here the denominator is showing that 8 parts make up the whole.\( \frac{a}{b+c} \)
You will learn
- Understand that fractions are parts of a whole
- Recognise fractions from shapes
- Be able to express fractions in words and numbers
- Be able to work out simple fraction problems
Formulae and Problem Solving
Learn about formulae and problem-solving method. Solving problems with one, two or three stages of calculations, problems that use different operations and problems in a range of contexts. This course is ideal for intermediate learners.
Introdution
A formula is a way of describing a rule or relationship. A formula can be expressed either in words using the word ‘equals’, or in symbols with an equals sign.The plural of formula is formulae.
Here are some examples of formulae from everyday life:
- 100 cm = 1 metre
- 10 km = 6.2 miles
- 10 km = 10000 meter
- 3 times 4 litres = 12 litres
- 100 pence = £1
Problem-solving method
To solve a number problem you must read the question first, and then work out if you need to add, subtract, multiply or divide.
Try using this 4 step method to help you solve formula problems:
1. Read and understand the problem – try to understand what the problem is about, and what you are being asked to do. Underline any key words.
2. Work out what calculations you need to do – Do you need to add, subtract, multiply or divide? Have you solved a similar problem before that can help you solve this one?
3. Carry out the calculations – Try to find the easiest way of working out the problem. Make sure you do all the steps needed to answer the question.
4. Check your answer – Use estimation to see if your answer is about right. Can you use a different method to check your answer, such as working backwards?
You will learn
- Solve problems with one, two or three stages of calculations
- Solve problems that use different operations
- Solve problems in a range of contexts
Division
Learn about division and understand that division is a method of repeated subtraction. This course is ideal for intermediate learners.
Introduction
Division involves sharing or grouping a number into equal parts.Division is the opposite of multiplying. When we know a multiplication fact we can find a division fact.
Division is the same as repeated subtraction.
For example 300 ÷ 4 = 75 , same as 75 x 4 =3000
In this example, 300 was subtracted 4 times, so ((300 ÷ 4 = 75)).
You will learn
- Understand that division is a method of repeated subtraction
- Understand key vocabulary used in division
- Be able to divide by 10, 100 and 1,000
- Be able to solve division problems in everyday settings
Numbers
Learn about whole numbers, recognising the value of digits in whole numbers up to the value of 10 million, stating the value of each digit in a seven digit whole number and ordering whole numbers up to seven digits in length. This course is ideal for beginners.
Introduction
We write numbers using only ten symbols, called digits. This means that all possible numbers (called figures) use a combination of the following digits: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9.Therefore where we place each digit when representing a figure is important. This is called place value.
The place value system allows each digit to represent a unit value in a figure:
· Ten millions
· Millions
· Hundred thousands
· Ten thousands
· Thousands
· Hundreds
· Tens
· Units
You will learn
- Recognise the value of digits in whole numbers up to the value of ten million
- State the value of each digit in a seven digit whole number
- Order whole numbers up to seven digits in length
Weight
Learn about weight, specifically solving problems requiring calculation with weight. This course is ideal for beginners.
Introduction
Weight is a measurement of how heavy something is.We measure weight using a mechanical or electrical device called a weighing scale. There are lots of different types of weighing scale. Here are some examples:
· Electronic kitchen scales for weighing food ingredients
· Brass scales with cupped trays
· Bathroom scales for weighing people
· A weighbridge for weighing lorries
You will learn
- Solve problems requiring calculation with weight
Volume and Capacity
Learn about volume and capacity, specifically solving problems requiring calculation with capacity and volume. This course is ideal for beginners.
Introduction
A dimension is a measurement in one direction.The number of dimensions is how many values are needed to locate points on a shape. For example:
· A point has no dimensions, only position
· A line has 1 dimension (length)
· A square has 2 dimensions (length and width)
· A cube has 3 dimensions (length, width and height)
3-dimensional shapes, also called 3D shapes or solids, have volume and capacity.
You will learn
- Solve problems requiring calculation with capacity and volume
Units of Measurement
Learn about units of measurement, specifically converting units of measurement in the same system. This course is ideal for beginnners.
Introduction
To be able to measure something, you need to know what unit to use. A unit is a general term that means a type of measurement.Units of measurement are standardised, meaning that there is a well-defined standard way to measure 1 of them.
A unit is any measurement that there is 1 of, such as:
· 1 metre
· 1 second
· 1 metre per second
· 1 gram
· 1 square centimetre
You will learn
- Convert units of measurement in the same system
Time
Learn about time, specifically converting between 12 and 24 hour times, converting between hours and minutes and problems requiring calculation with time. This course is ideal for beginners.
Introduction
For example, twenty past nine can be written in the following ways:
· 9:20 (using a colon – there is a colon between the 9 and the 20)
· 9.20 (using a full stop)
Time is a non-decimal system. This means it is not measured in tens. For example:
· One day is 24 hours
· One hour is 60 minutes
· One minute is 60 seconds
Because of this, you need to be careful when making calculations that involve hours and minutes.
You will learn
- Convert between 12 and 24 hour times
- Convert between hours and minutes
- Solve problems requiring calculation with time
Temperature
Learn about temperature, specifically solving problems requiring calculation with temperature. This course is ideal for beginners.
Introduction
Temperature refers to how hot or cold something is.Temperature is measured in degrees. The symbol for degrees is a small circle that sits slightly above the number in temperature.
The two most common scales are Celsius (abbreviated to a capital letter C) and Fahrenheit (abbreviated to a capital letter F). In the UK, we usually measure temperature in Celsius.
On a standard thermometer, the left hand side measures temperature in Celsius, ranging from 0 (freezing point) to 100 (boiling point). The right hand side measures temperature in Fahrenheit, ranging from 32 (freezing point) to 112 (boiling point).
You will learn
- Solve problems requiring calculation with temperature
Subtraction
Learn about subtraction, specifically subtracting whole numbers using a range of strategies. This course is ideal for beginners.
Introduction
When you subtract numbers you use the subtraction sign. It is a small horizontal line.We use different words to describe subtraction.
For example, can be described as:
· 15 subtract 6 equals 9
· If you reduce 15 by 6 you get 9
· The difference between 15 and 6 is 9
You will learn
- Subtract whole numbers using a range of strategies
Rounding and Estimating
Learn about rounding and estimating, rounding numbers to the nearest 10, 100 or 1000 and using rounding to estimate basic calculations. This course is ideal for beginners.
Introduction
Rounding numbers is a way to get a rough idea or an estimate. An estimate might be a littlemore or a little less than the exact figure. Rounding means making a number simpler but keeping its value close to what it was.
Although rounding won’t give you an exact figure, by carrying out an estimate you can check that the answer to a problem is sensible. For example, it’s a good idea to estimate the answer first when using a calculator in case you make keying errors.
Estimation is also really useful with multiple-choice test questions. It helps you decide which option is the correct answer, before checking by carrying out calculations.
3 of 21 – Benefits of rounding
Rounding is a really important tool with a number of benefits, such as:
· Making it easier to describe and understand numbers
· Making calculations easier
· Making it easier to estimate answers
· Helping you to identify mistakes in maths work
· Being useful when you don’t need an exact answer
You will learn
- Round numbers to the nearest 10,100 or 1000
- Use rounding to estimate basic calculations
Ratio
Learn about ratio, specifically writing ratios in their simplest form and solving simple problems involving ratio where one number is a multiple of the other. This course is ideal for beginners.
Introdcution
Ratio tells us the size of two amounts compared to each other.Consider four squares – three of them are blue and one of them is yellow. Here are three ways that we can express this as a ratio:
· We can use a colon to separate the values. For example, 5:1 (the colon is between the 3 and the 1).
· We can separate the values with the word ‘to’. For example, 5 to 1.
· We can write it as a fraction. For example, \( \frac{5}{1} \) .
You will learn
- Write ratios in their simplest form
- Solve simple problems involving ratio where one number is a multiple of the other
Probability
Learn about probability, specifically calculating one stage and two stage probability events. This course is ideal for beginners.
Introduction
Probability refers to the likelihood or chance of something happening. It can be helpful to think of probability as a scale, ranging from the certain to the impossible.The probability scale is a line with impossible things at one end and definite things at the other end. In the middle are things that are just as likely to happen as they are to not happen; we call this an even chance.
Here are some examples and their positions on a probability scale:
An example of something that is at one end of the scale and labelled impossible could be: ‘It is impossible to win the lottery if you haven’t bought a ticket!’.
The chances of any event can be shown on a probability scale from 0 to 1.
A probability of 1/2 tells us that the event has an even chance of happening.
You will learn
- Calculate one stage and two stage probability events